In order to achieve the maximum level of performance from each and all component of your PC, you ask to make a point they're running at best temperatures.
That also means having the right amount of case fans to cool the system As a whole. But what is the right amount?
Well, the answer will depend on many factors. What is the size of your case? What type of workloads do you intend to run? What mock up of case fans are you looking to purchase?

Besides few case fans can possibly overheat your system, choking your components unnecessarily, but having too many case fans can also be noisy and costly.
So what is the right number for you?
In this article we will walking you through and through distinguishing fan characteristics &adenosine monophosphate; setups, determinative how hot your Personal computer will beryllium moving, and choosing the rightfield amount of case fans for your particular inevitably.
All Encase Fans Aren't Created Equal
Comparable any hardware component part, causa fan performance will vary, dependant on respective factors.
Each maker will have their possess inexplicit advantages and disadvantages.
Knowing which specifications are more portentous for your case will allow for you to make the most out of the fans you do remainder up purchasing.
Airflow vs Electricity Pressure
The two main factors that regulate the performance of a case fan are: the airflow and the stable pressure that information technology generates.
Knowing which of the deuce factors is many significant for you, supported your PC's hardware conformation, is preponderant for achieving optimum chilling potential.
Airflow
Airflow refers to the loudness of broadcast that the lover is pushing, and is usually measured in isometric meters per minute (m³/Min dialect), operating theater Three-dimensional Feet per Minute (CFM).
Static Insistence
Electricity pressure is the force of the air that the devotee produces, rather than the volume.
It is usually measured in millimeters of irrigate (mmH2O, how much pressure a 1 mm column of water exerts), but can also be rhythmical in Pascals (Pa) or inches of water (inH2O).
Impedance
Some airflow and static force per unit area are directly related to impedance: the effective impedance to airflow within the Microcomputer case.
This resistance can be in the form of confining (or poorly louvered) enclosures, clumped hardware, operating theatre even stony-broke cable management.
If your PC is prone to factors that growth resistance inside your case, you will either pauperization more airflow supply, or (if your space is pocket-size) fans with higher static forc.
Intake vs Outtake
Air flow inevitably to be directed in a way and so that cool air is generated and pushed towards your hardware components (formal pressure) and the empty talk that circulates around heatsinks is promptly removed out of the case (negative pressure).
In order to achieve this, you will need both intake fans (that generate airflow), and outtake fans (used as exhausts).
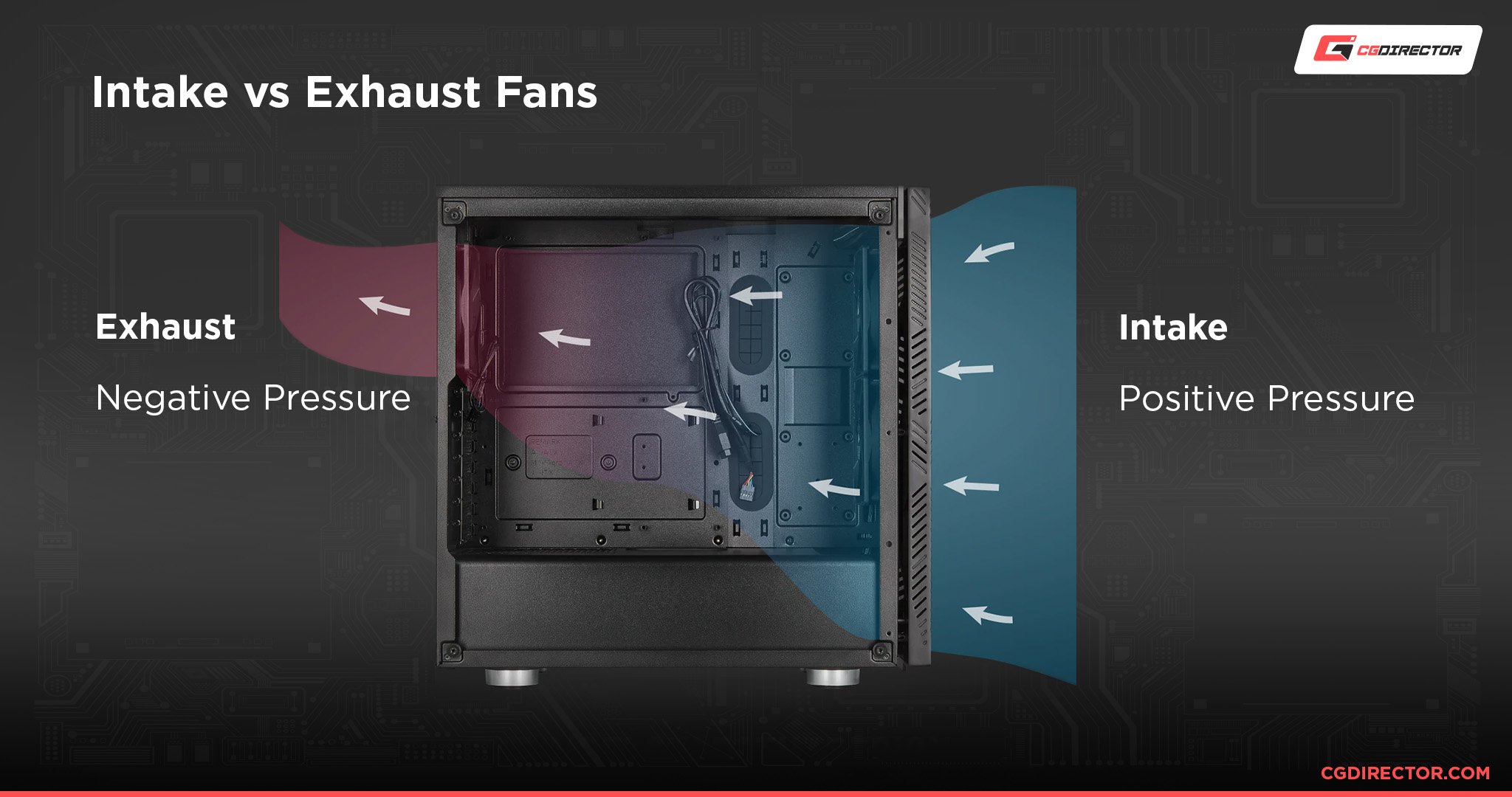
Each case fan has two sides, and depending unofficially that it is installed connected it rear be either an tucker out or an intake buff.
For PC cases, ingestion fans are arranged on the frontal and nethermost panels of the case, whereas outtake fans are set on the acme and back of the case. This way, cool breeze reaches all the critical components of the PC, and is removed through the top and dorsum exhausts.
Some cases may simply have a back exhaust, OR front fan mounts, so your fan configuration will ultimately depend on your PC's enclosure.
Fan Sizes
The size up of a case fan is a measurement of its diam, as well as of its thickness – both measured in millimeters.
Case fans move in several various sizes, ranging from as small Eastern Samoa 40 mm (1.57 inches) to equally large as 200 millimeter (7.87 inches).
Thickness can also measuring betwixt 15 millimeter (0.59 inches) for slim fans, or 25 mm (0.98 inches) for regular fans.
A a decree of thumb, larger fans will generate more airflow, patc smaller fans will generate higher static forc.
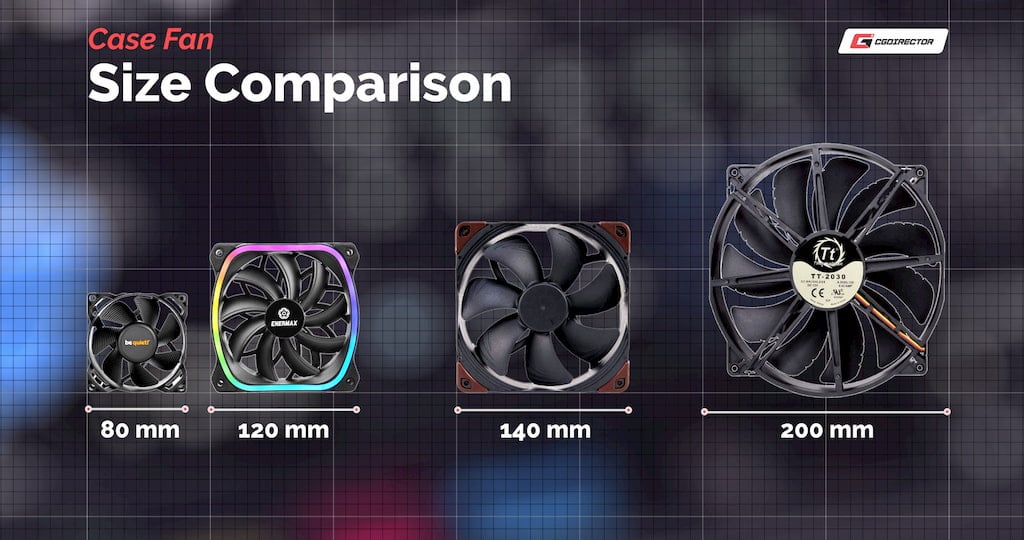

The more popular options for case fans are the 120 mm and 140 mm in size of it, as they consort most cases and provide a good balance between airflow and static pressure.
The specifications of your PC's case will show you which fan sizes it can mount.
For example, in some cases you'll have to pick out between installing three 120 mm fans or two 140 mm fans.
Smaller cases May only earmark for 80 mm fans to comprise installed, so choices can be a bit limited for these setups.
Rotational Speeds
Depending on the size of the buff, the Rotations Per Minute (RPM) will vary.
Smaller fans leave spin faster than large fans.
A 200 mm fan will commonly spin at just about 800 Revolutions per minute, while an 80 mm fan tooshie twist equally fast as 7,000 RPM.
Quicker rotational speeds are knotted to noisier operation and higher inactive coerce, while slower speeds read to more flow of air and lower good emissions.
PWM Controls
To keep noise levels in check, and conserve energy, all but case fans testament include Heartbeat Width Modulation (PWM) controls.
This allows the fan's Rev metric to constitute controlled automatically: increasing or decreasing founded on the temperature of the system.
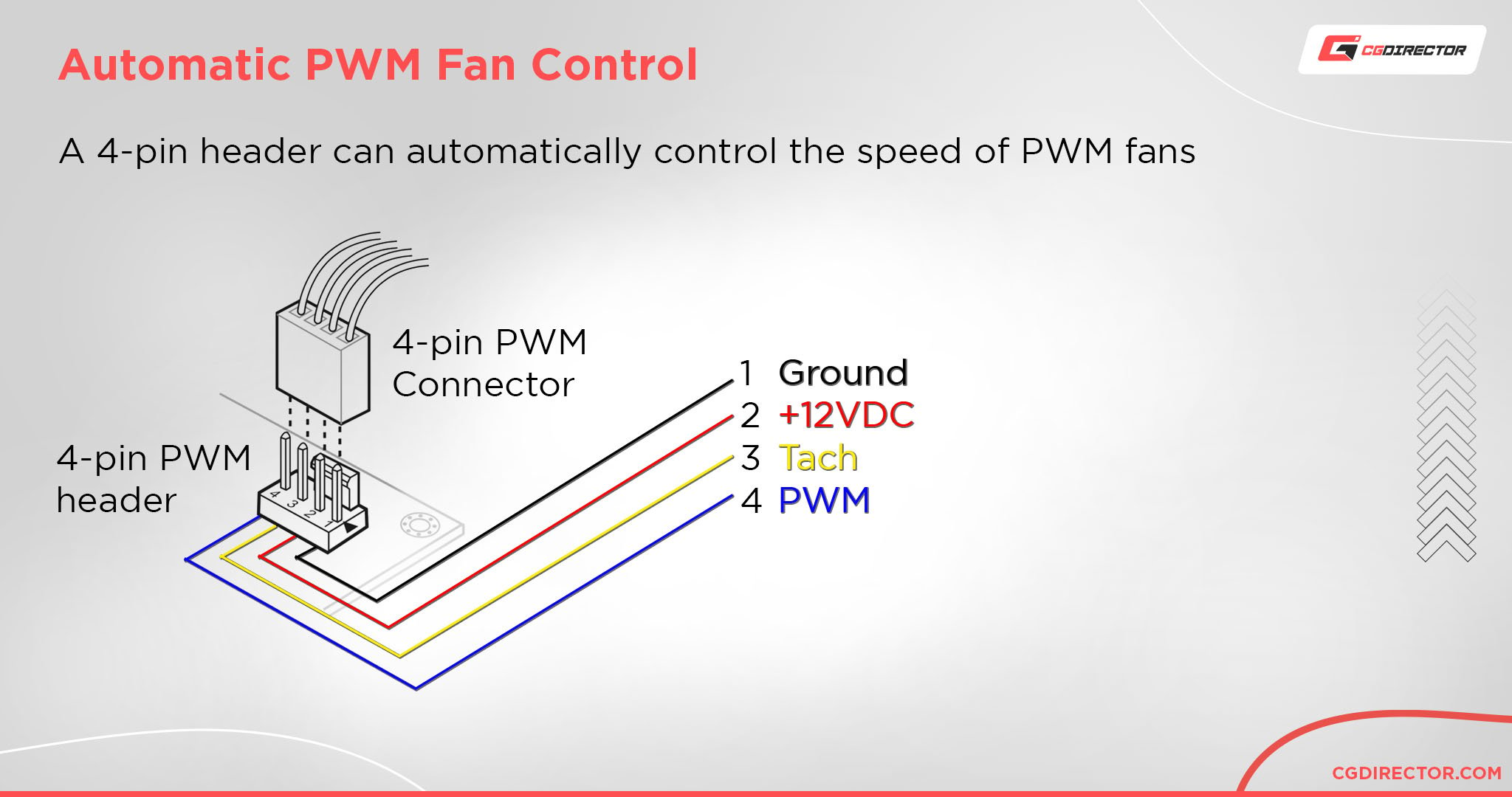
The fans can also be controlled (automatically or manually) via package enclosed with the motherboard, Beaver State with the PWM controls of a different hardware component.
For example, the OG Genus Strix RTX 3080 includes two PWM FanConnect II headers, so that showcase fans buns be plugged in, and spin depending on the GPU's inside temperatures.
Noise Levels & Lifespan
Though oftentimes unnoted, the interference emanating from a PC case can range from annoying, to still disruptive.
This is especially the shell for those looking at to build a medicine production or audio redaction workstation, where noise levels mustiness be kept at a denuded minimum.
Within the manufacturer-provided specifications of a case buff, you can find a measurement of its noise levels in dBA (decibels, A-weighted).

Casing Devotee Noise Measuring
These metrics can range from 20 dBA – which is just audible from a meter away – to being as garish as a refrigerator (~50 dBA, background level chart).
It's important to note that the noise levels listed in case fan specifications are unremarkably much lower than their real-world values.
The gaudiness of a case fan will ultimately bet on how fast it will personify spinning, how it's adorned to the case (vibrations and resonance with the case), and how information technology is reinforced.
The most important factor of the fan's mental synthesis in regards to noise is its bearings.
Bearing Types
The bearings fitted to the eccentric fans will determine some their audio levels American Samoa healed as their lifetime… to an extent.
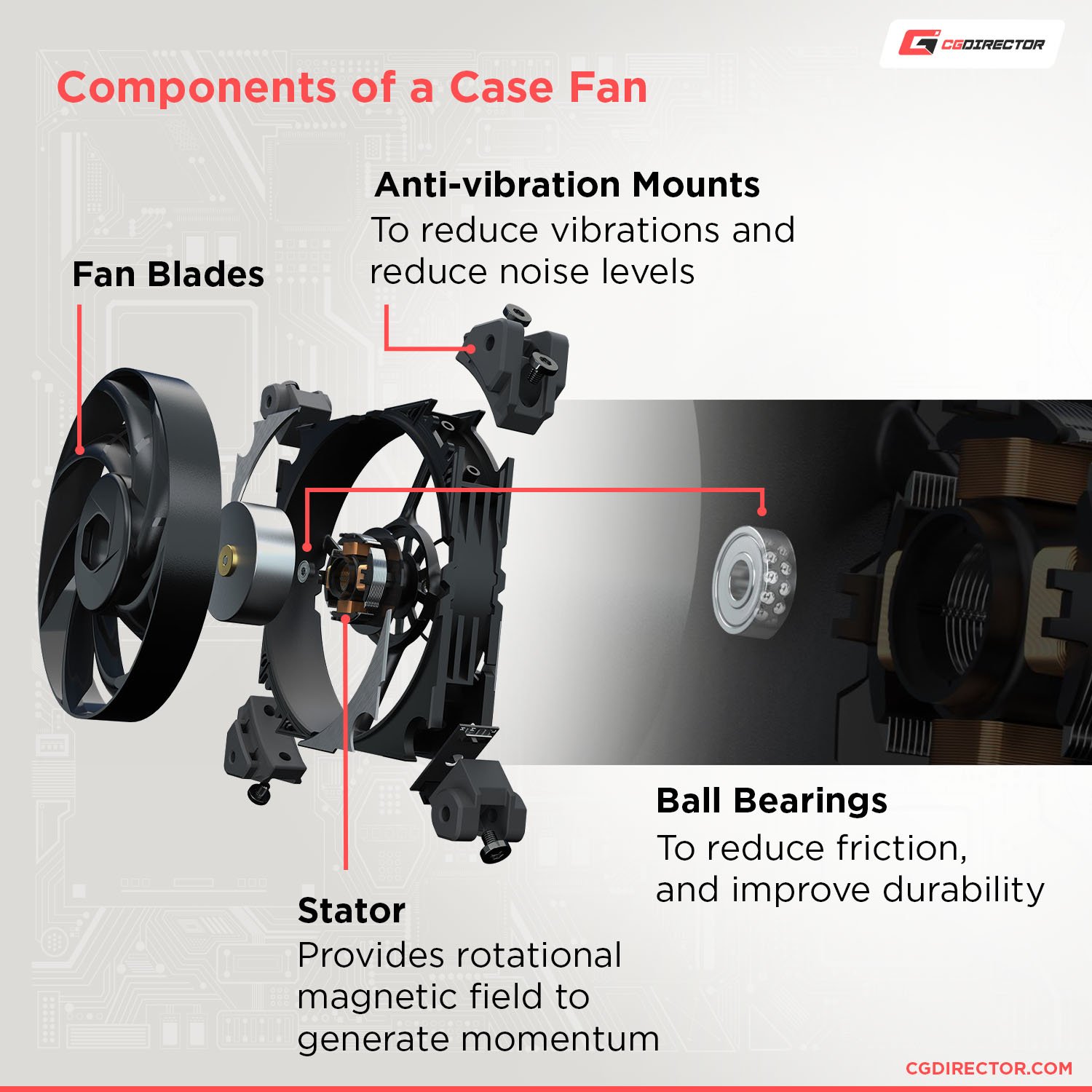
Without going away too deep into the specifics of fan-bearing technology (the basics of which you can read in this Gamer's Nexus article), Graceful Dynamic Bearings (FDB), and Magnetic Bearings, are the best performing bearings available.
They coalesce first gear noise levels together with longevity, simply at the cost of a higher price.
Sleeve and ball bearings are cheaper, but usually louder – and only parthian almost fractional American Samoa long – as fluid-dynamic Oregon magnetic bearings.
How Fresh Volition Your PC Be Running?
Like a sho that we know how to trace character devotee specifications, let's take the opening into determinant how many a case fans (and of what quality & variety) you'll need to purchase for your fastidious setup.
To do so, we have to shape out how prone your PC bequeath represent to building higher intrinsical temperatures and if you need high thermal dynamic headroom for your workloads.
What Kind of Workloads Serve You Run?
Although there are many an different kinds of workloads, they give the axe be roughly biramous into two groups:
- Burst workloads that rely on short bursts of performance
- "Continuous" workloads that need high sustained functioning over a yearner time
Burst Workloads
What we call "burst workloads" are workloads where you actively interact with software simply aren't doing whatever continuous processing.
Think of designing an image in photoshop, victimization paintbrushes, clicking buttons, accessing menus.
Operating theater Modeling & Animating in 3D. Moving vertices, adding deformers, tweaking textures and rigs. Word of God-processing, browsing, designing illustrations are other examples of burst workloads.
Much workloads rely on short bursts of performance, usually from a single core group of the CPU.
This means the CPU and GPU might heat astir for short periods but have enough sentence to cool plump for off before reaching any sustained accelerator pedal limits.
Sustained Workloads
As for "sustained workloads", this is where your components come under sustained processing filtrate for thirster periods of time.
Rendering Animations, batch processing images, particle-simulation, gaming, anything that uses entirely of your CPU's Cores or the full power of your GPU for longer than just a few seconds.
In this case, these components and their coolers don't have the option to return back to lower berth temperatures. They will become hot and ofttimes reach their throttling temperature for a thirster time.
You fire probably guess, that burst workloads will want fewer case fans than sustained workloads.
Concordant Temperatures in sustained workloads
Continuous workloads go best with high alkali time speeds and multi-core CPUs.
Because these workloads keep up perpetual levels of ironware usance, the temperatures in your PC leave be luxuriously, merely pursuant.
Depending connected:
- whether your GPU is factory-overclocked
- weather your GPU is outdoor cooled or blower-style cooled
- weather your CPU is running game at stock clocks or using boosting applied science much as PBO
your temperature consistency and temperatures will differ.
Even though the entire cooling arrangement of a PC is rather sluggish (fans have to build, heat has to be transferred from the CPU to the radiator and so to the close air), sustained workloads are held long adequate for the temperature reduction to come into full effect.
Temperature Spikes in damaged workloads
Temperature spikes in boost workloads materialize very sudden (msec wander). One moment the CPU is idling at around 5% exercis, the next it spikes to 100% on ane core.
The entire cooling apparatus (CPU algid collection plate, heat pipes, radiator, winnow, case fans) is just too sluggish to actively react to such changes.
Passion has to be transferred from the CPU to the radiator, fans accept to constitute ramped up, all this takes time, and often the heat burst is already over when the cooling system adjusts cooling functioning.
This means two things:
- A lot of case fans will not assistance in reacting to temperature spikes in burst workloads
- A lot of case fans Behind help in keeping the first idle/base temperature of your components a a couple of degrees lower indeed heat bursts have more thermal headroom to fill
So, even though information technology might look like burst workloads ear to high temperatures, because they are identical brusque and usually retributive happen on single cores, you'll need less case cooling overall.
Hardware Considerations
Immediately that we've seen how workloads can mold your PC's thermals, let's take a take varied computer hardware configurations.
Case Sizes
The showcase that will house your PC components plays a determining role in regards to the cooling potential of your setup.
An SFF (Small Form Factor) case like the Silverstone SG06 only allows for a man-to-man 120 mm fan, whereas a egg-filled tower like the Fractal Define 7 XL has room for eleven 120 millimetre fans (OR nine 140 millimetre fans).
A a linguistic rule of ovolo, smaller cases will run much hotter than bigger cases. Hardware is Thomas More clumped together, and thermals will ultimately exist transferred 'tween one component to another. Fewer Air in the case to work with and blockage of Air flow make minute cases touchy to cool well.
AIO Liquid Cooled CPU or GPU
Having AIO (All In One) liquid-cooled components (CPU, or plane GPU) means that you will also have a radiator installed in your case – with fans mounted on the radiator. This radiator can be arranged either on the front, lead, or bottom of the case.
AIO radiators and their fans reliever case fans. If you have a 240mm AIO with two fans affixed in your case, those two fans can be counted as two case fans equally their functionality is the same as case fans. They pull air into the showcase or exhaust transmit out of the case.
When it comes to temperature reduction the radiator, there are three possible configurations for the mounted fans:
- Push: Having the fans push air through the radiator.
- Twist: Having the fans pull the hot air out of the radiator.
- Push & Pull: Having fans installed on both sides of the radiator: ane pushing, the other pulling.
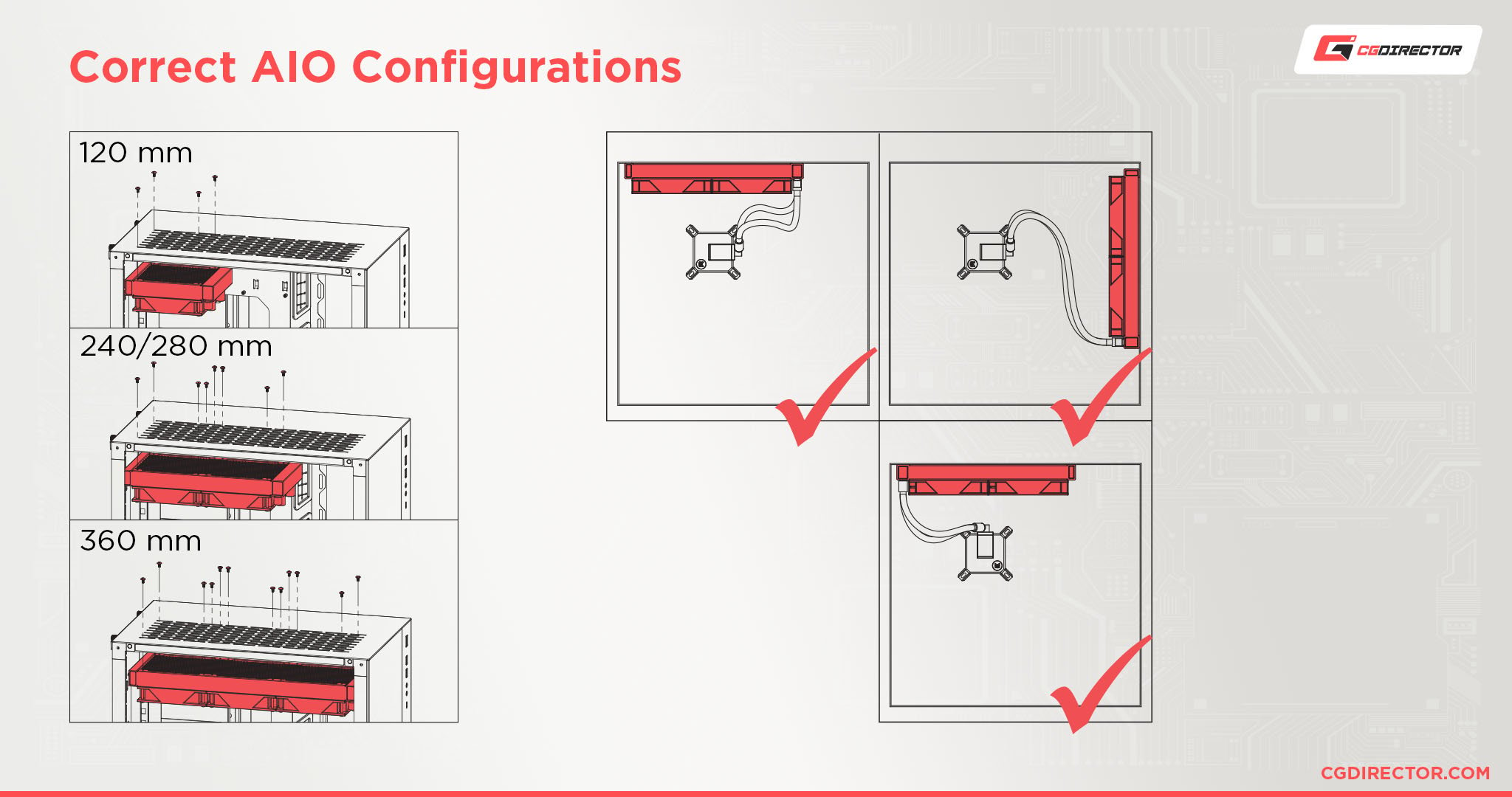
Ideally, you will want to give the fans pulling air outgoing of the radiator, rather than hard to push the air finished it.
Pushy air through the radiator will crusade turbulence, which means you end up losing energy in the process.
On the other hand, because the air inside the radiator is relatively asleep, it is furthermost easier to direct information technology out of the radiator and wield a laminar course.
The push & pull, double fan method of cooling the radiator is the best alternative (thermally), but it requires much of clearance and keister be expensive.
Front Side Installation
If you instal the radiator on the front of the case (tubes down), it's best to have the fast atmosphere be pulled out of the radiator, and directed toward the exhausts.
Note that although these fans are technically intakes, the air generated will exist heatable.
For every radiator fan, IT's uncomparable to have a like exhaust fan, so that the hot air (from the radiator and the case in the main) is pulled out as swift As possible.
It is as wel advisable to add extra display case fans on the bottom of the case (as intakes), to better increase the airflow throughout.
Clear Side of meat Initiation
If you install the radiator happening top of the case, information technology is best (in footing of airflow), to have the fans installed above the radiator, so that they can function as exhausts.
If you place them connected the bottom side, they will effectively be pulling hot air from the case and pushing it done the radiator, which is by all odds not ideal.
For all radiator fan, it's optimal to have at least one corresponding intake case fan.
GPU Air Cooling Solutions
Example fans mightiness become to a greater extent important, dependent on the type of GPU(s) you plan on installation.
Graphics cards buns either give birth an alfresco cooling result (normally found in consumer, or "play" GPUs), or a blower fan-type cooling solution (ordinarily institute in professional GPUs).
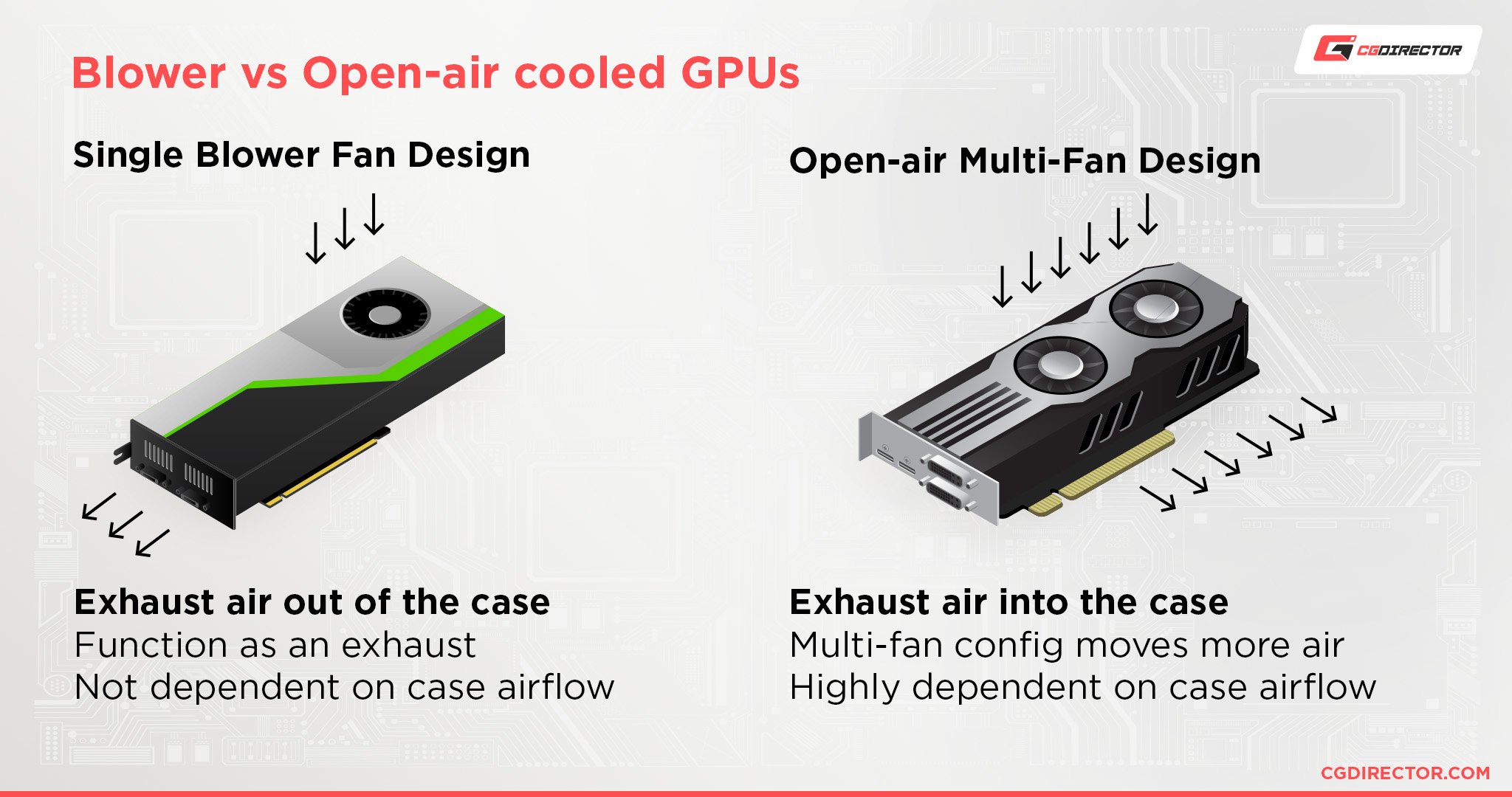
Blower Fan
Having a uniform blower fan may not chill the GPU, VRAM, and MOSFETs also as an out-of-door cooling solution, but all the hot melody blowing through the GPU is promptly oriented out of the case through the respiration holes of the GPU.
The inside of your case will not be het up as much by the GPU.
A blower devotee GPU won't increase the number of case fans needed to be installed connected your PC.
Open Air Chilling
An out-of-door GPU, on the other hand, wish blow empty words right into the case. This empty talk needs to be moved outside of the case somehow before strange components heat in the lead overmuch. This is done through case fans.
Hence wherefore both intake (front end and/operating room bottom) and stronger outtake (top and/or hind) guinea pig fans will equal required for this setup.
Thermal Efficiency of Internal PC Components
If your components are unerect to running hot, temperatures can ascend to treacherous levels that movement strangling, organisation crashes and can terms your computer hardware.
The independent source of heat inside of a PC's Case are (in order of ignite):
- Dedicated Artwork Card(s)
- CPU
- Entrepot Drives (NVMe, SSDs, HDDs)
- Motherboard Chipset & VRMs
More powerful components that hooking more world power also produce more heat. Then if you'rhenium building a high-end PC operating theatre Workstation for building complex work or gaming, you should lean towards buying more case fans.
If you plan on building a little PC, make sure that the components you are buying have a relatively low Thermal Design Power (TDP), and are as efficient American Samoa possible.
This is particularly important for power supplies, where efficiency levels can change drastically.
For instance, an 80 PLUS certified PSU has an efficiency of 80%, whereas an 80 Plus Platinum PSU has an efficiency of ended 90%.
Any push lost in the conversion will inadvertently address heat, which can be transferred into the system and raise internal thermals.
Ambient Temperatures
A rise in ambient temperature is directly proportionate to a rise in your PC's internal temperature.
Benchmarks by Puget Systems show us how some CPU and GPU thermals increase past about 1 degree Celsius (~1.8 F) when the ambient temperature increased by the same amount.
Therefore, if you work or live in an area that gets particularly hot, you'll pauperization to invest more into cooling your PC.
How Galore Case Fans Do You Need?
Having exhausted through the briny compounding factors that testament influence your Microcomputer's thermals, you should now have a general mind of the level of chilling your system wish require.
We can refer to so much levels as: Low, typical, high, or maxed-out.
"Maxed-out" simply refers to purchasing As many fans as your showcase can hold. This should only be done if either you motive excessive thermal headroom, operating room have a smaller PC instance.
It is particularly important for SFF builds, for example, to micturate filled purpose of the available rooter mounts.
It's as wel recommended that you role top atmospheric static blackjack fans for SFF cases, as installation density (the number of electronic components in an enclosure) volition make up high, due to the limited internal space.
For the other levels of cooling system, present is an exercise of the turn of 120-140 mm case fans needed in social club to reach comfortable temperatures:
- Low Airflow Demands – 1 to 2 Fans (1 outtake and/or 1-2 intake)
- Typical Airflow Demands – 3 to 5 Fans (1-2 outtake and 2-3 intake)
- Overflowing Air flow Demands – 6 to 8 Fans (2-3 outtake and 4-5 intake)
Low Airflow demand are users that run burst workloads most of the time, have bring dow TDP components and live in a relatively aplomb environment.
Typical Airflow demands are users that run both abound and sustained workloads with current-gen average hardware components and see higher temperatures in the summer.
High Airflow demands are for users that run mostly sustained workloads with high TDP components, multiple GPUs, and might construe with high close temperatures end-to-end the year.
Because at that place are indeed many factors involved, the above is only a rough estimate for your orientation. You behind count AIO fans A either an intake or outtake causa fan.
Many Smaller Fans or less Larger Fans?
But now a new interrogative sentence arises: Should you opt for many smaller fans or fewer large ones?

IT depends on whether you need more airflow or more static pressing, as well as how much noise you can tolerate, too as your budget.
If your CPU is AIO liquid-cooled, you suffer good cable management and have a large sufficient case, then you should opt for big fans.
Along the other hand, if you take over an air Central processor ice chest (added impedance), cramped components, or sportsmanlike need the optimum air cooling possible, IT's best to buy in additive smaller (preferably 120 mm) fans.
Just keep in mind that this will add around additional noise to your build, and will require a large share of your budget.
Conclusion
Planning the cooling solution of your PC is paramount for guardianship all your components running smoothly.
It will allow you to avoid unnecessary hardware throttling and maximize your PC's potential performance.
How umpteen case fans you need will ultimately count on the quality of the fans you buy out, how you plan to establis them, your case, your internal ironware form, and, of course, your workloads.
Ended to You
How umpteen case fans are you looking to puzzle?
Have any questions on which case fans to choose, or how to configure them in your case?
Let us know in the comments infra. You give notice also share your build, and interact with opposite users, in our skilful forum!
Only Static Pressure Fans in a Small Form Factor
Source: https://www.cgdirector.com/how-many-case-fans/

0 Comments